Vol 9: Forget Cryptocurrencies can Blockchain Technology revolutionize our world?
A beginner's guide to understanding Blockchain.
Blockchain! The word that seems to be on everyone lips these days. One of the biggest technology since the internet, a revolutionary technology that will remake the future of manufacturing to logistics, transportation, healthcare and real estate, every sector, every industry is set to undergo a radical shift in the next few years all because of this technology called Blockchain. A network that allows every client on it to reach a consensus without having to trust each other.
Yet we do not understand blockchain to an extent where we could really grasp all the ideas about it. To date, technology has been a domain of computer programmers, experts and leaders in our world political space, when the Internet came, it came as a technology of centralized authority, but blockchain is different, blockchain is a technology that will democratize the world tech ecosystem, in other words, each user will have power over its own data because members of the community would own and operate the infrastructure used for storage and computing. This would take away control from government or corporate bodies.
So What is Blockchain?
Let me start with this example;
Debby wants to buy a cup of coffee from John. John is going to sell the cup of coffee for a price of $5, upon agreement, the transaction details will be recorded in a ledger, this is exactly the principle behind Blockchain.
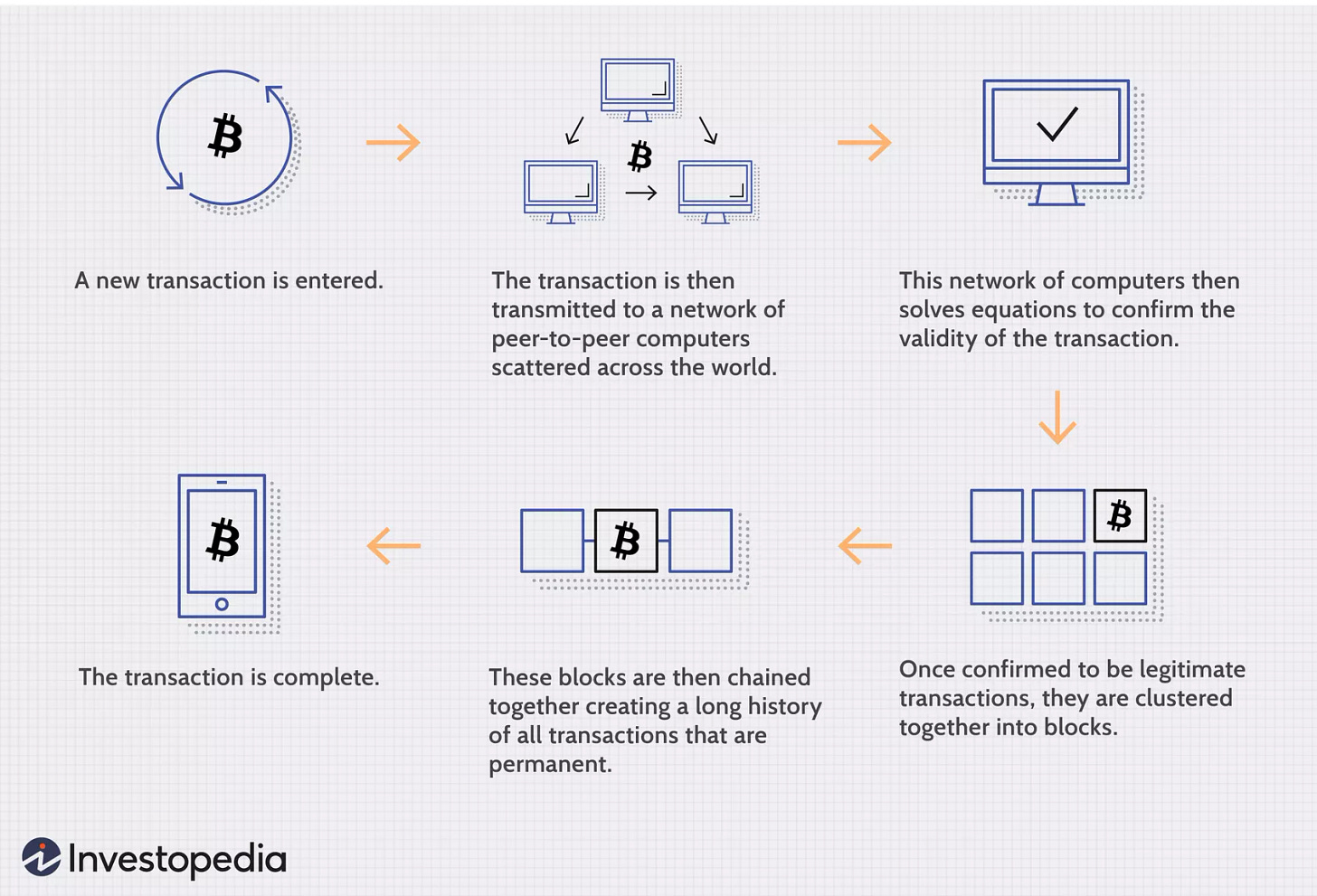
Blockchain is a decentralized database, a digital immutable distributed ledger, that can be programmed to record and track anything of value, from financial transactions to medical records to supply-chain management etc. It uses a technique called Cryptography to process, and verify every transaction on the system before making any change which leads to the creation of a new Block, thereby making them secure, permanent, and transparent. It was specifically designed to be decentralized and stores information permanently across a network of personal computers, this not only decentralizes the information but also distributes it too reducing the ability for data tampering which creates trust in the data.
Blockchain is all about Databases, it is a non-destructive database. Databases are an organized collection of structured information or data stored on a computer that can only be accessed electronically from a computer system.
What do we mean by Block in Blockchain?
A Block can also be called a digital record, they are where data are stored on a blockchain, they contain some whole number of records, having a maximum capacity, any new information to be added is put into a freshly created block and the immutable chain continues to grow. It’s up to whoever is making the blockchain to determine what kind of data they can store in the block. For cryptocurrencies, blocks contain the records of valid transactions that have taken place on the network.
What do we mean by Chain in Blockchain?
Imagine I just created a new Blockchain: the first block would be there, you know, lonely, but after creating the first block, the second block would come along and say, “the block before me is the first block,” the next block would say “the block before me is the second block,” and so on. Now the linking of other chronological blocks to form a continuous line metaphorically is called a chain of blocks, the linking is the Chain.
How did It start?
The Idea behind blockchain technology goes back several years before Bitcoin the famous cryptocurrency, it was first outlined as early as 1991 by two research scientists named Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. They published their research on cryptographically secured blocks in the Journal of Cryptography with the title “How to time-stamp a digital document.” Both of them wanted to implement a computationally practical solution where digital documents could be time-stamped so that they could not be tampered with. Their paper brought to the world stage the first sequence of immutable chains of digital documents whose timestamps could not be fraudulently changed.
The system they created used a cryptographically secured chain of blocks to store the time-stamped documents and in 1992, Haber, Stornetta, and Dave Bayer incorporated Merkle trees into the design, named after the computer scientist Ralph Merkle, which improved its efficiency by allowing several document certificates to be collected into one block.
In 2002 decentralized trust within a network system was conceptualized, by now, experts were already discussing how cryptography and “blocks” should evolve to generate the innovation of a decentralized network file system that not only included cryptographic time-stamping signatures on documents but also a network file system based on trust between two “block writers.” These innovations were published in 2002 at The Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing by David Mazieres and Dennis Shasha.
Everything mentioned until this point laid the foundation for the first real blockchain application. It was in 2008 that the technology started to gain relevance, Satoshi Nakamoto (a pseudo name of a person or a group of people) published a white paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” In the whitepaper, he provided details of how the technology was well equipped to enhance digital trust given the decentralization aspect that meant nobody would ever be in control of anything.
On the 3rd of January 2009, the first Bitcoin block (also called the “Genesis Block”) was mined by Satoshi Nakamoto which had a reward of 50 bitcoins, it was the start of the digital revolution. The first recipient of bitcoin was Hal Finney he received 10 bitcoins from Satoshi Nakamoto on the 12th of January 2009, this was the first bitcoin transaction. For the first time in history the invention made it possible to send money around the globe without banks, governments or any centralized form of organization, cryptocurrencies now promise to create a new decentralized financial system beyond the control of government and banks and it has already captured the imagination of the world.

Where we are going with it.
While the technology is most famous for its role in promoting the rise of digital currencies over the past several years, there are also many other non-crypto currency uses and applications for this technology. It will be virtually used for anything of value that can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved. It will transform our interactions with each other, cooperation’s, the underlying centralized infrastructure.
The biggest effect of Blockchain might be in financial services, especially with the growing movement toward decentralized finance. According to a World Bank report in 2017, over half the population in the world did not have access to a bank account in 2009 and over two billion people today remain without a bank account, these and more are some of the issues blockchain is trying to solve.
It will help in creating a global online database that anyone, anywhere in the world with an internet connection can use. Unlike traditional databases which belong to central figures like banks and governments, a blockchain doesn’t belong to anyone. At their core, Blockchains let you agree about data with strangers on the internet, it helps you fill the trust gap, you can make money transactions with anyone, anywhere in the world without having to know or see each other.
The period we are now in experimenting Blockchain technology is like the early days of the internet, experimenting now to revolutionize how the world works later, although its popularity came from around cryptocurrency, experts say Blockchain could revolutionize how our society works. Governments will also likely continue to embrace blockchain. As universities, governments and private corporations continue to research and invest in blockchain, the technology will only improve, but they must first address the challenges that blockchain brings, particularly regarding security, energy, privacy and scalability.
The thing about great inventions like this is that we don’t know what the future is going to become of them at their early stage, we only have hindsight years later to fully understand their growth and impact on us. Hindsight is easy, foresight is very difficult. Let us take a look at some of the past inventions that revolutionized our world;
The Printing Press in the 1400s, before the invention of the printing press, sound learning and knowledge was only for the privileged in the society, the printing press was invented and completely closed the learning and knowledge gap.
The Steam Engine came and change how we work, the labour work and manufacturing process was largely done by slaves, the invention of the steam engine helped to drastically reduce slavery and colonialism.
Our favourite invention, the Internet which started 40 years ago, came and revolutionize the information sector and the way we communicate, the world is now a lot smaller than it was 40 years ago.
I see Blockchain as the printing press, the steam engine, and the internet of our time. Indeed, some blockchain experts believe that the technology could far outperform cryptocurrencies themselves in terms of its overall impact and that the real potential of blockchain is yet to be fully discovered. Apart from it being linked with a specific cryptocurrency, we are going to see it being utilized in many areas of other applications.
To end this, let us imagine a world where;
You control your own money, not banks
You can send money to anyone, anywhere in the world for almost no cost and almost instantly.
Your shipments are automatically monitored and safe, reducing time, costs, labour, emissions.
Implementing a blockchain-based government system can significantly reduce bureaucracy and corruption and make the government more open in its decisions, giving room for transparency and efficiency of governmental operations. For example; The UAE Government adopted blockchain technology in conducting its transactions. To aid this move, it launched the Emirates Blockchain Strategy 2021 and Dubai Blockchain Strategy. You can read more about that here The Emirates Blockchain Strategy 2021.
Where we have a decentralized cloud storage, avoidable of hacking, human error and data loss.
Imagine a world where blockchain technology will be used for voter registration, identity verification and electronic vote counting to ensure that only legitimate votes are counted and no votes are changed or removed, making elections fairer and more democratic, when electoral results are been viewed on a publicly immutable ledgers.
Blockchain can help to streamline and make it more secure to distribute welfare or unemployment benefit etc. to the public because it is accessible and verifiable on the system to the public. GOVCOIN a U.K based startup is working with governments to help distribute public benefits using the blockchain.
A world where Healthcare centres can store medical records safely on the blockchain and only share them with authorized doctors or patients. This will improve data security and can even help improve the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
Guess what, we are already living in that world, that is what Blockchain is already doing. I just listed a few sectors here, it cut across almost all sectors, future use cases will be Energy management, Retail, Generating patents, Real-Estate, Online music, if your field deals with data and transactions in any way, it is likely a field that can be disrupted by blockchain, the difference is you don’t have to trust a central authority, it is done out of trustless basis. The possibilities of this technology are endless, this is the future, where we go from here is really up to all of our imaginations.
Until next time, Happy Learning.
Enjoy your weekend.
Faith.






Nice job. Its hard to find a self explanatory post on blockchain
Arguably the simplest explainer for Blockchain technology here. And I'm not less impressed by your writing style, too. Easy reading. I just buried my head in my phone for like 10 minutes reading this article, line by line, detail by detail.
I was tempted to screenshot some lines, but if I'd done that, I'd have ended up having the whole article nested in my Gallery app.
Great piece, Michael.